Effective Guide to How to Calculate Price Elasticity of Demand in 2025
Understanding Price Elasticity of Demand
Price elasticity of demand measures how sensitive the quantity demanded of a good is to changes in its price. A fundamental concept in economics, **calculating price elasticity** is vital for understanding **consumer behavior** and assessing how **price changes** affect market dynamics. In today’s economy, the concept’s relevance extends beyond theoretical application, influencing **demand pricing strategies** and guiding businesses in making informed decisions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to effectively calculate price elasticity, starting with an outline of the elasticity formula and its significance in market analysis.
What Is the Elasticity Formula?
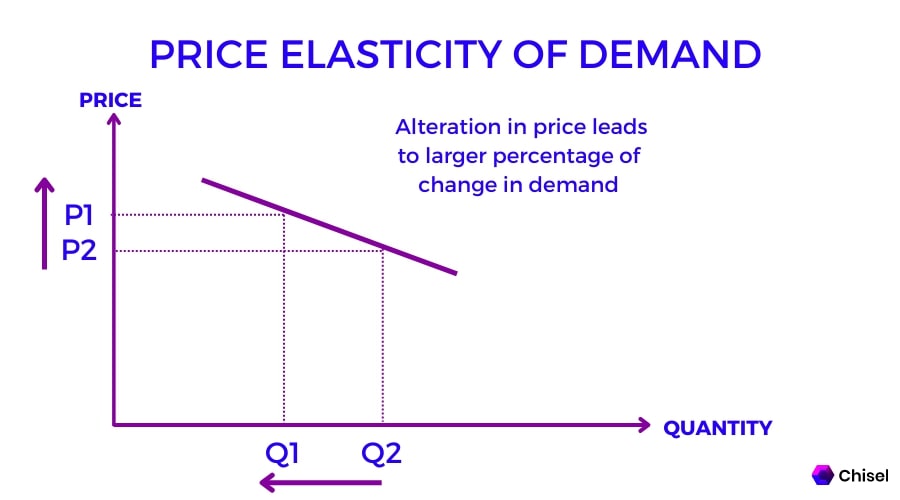
The elasticity formula is crucial for quantifying consumer responses to price fluctuations. It is expressed as: Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) = (% Change in Quantity Demanded) / (% Change in Price). This formula helps in evaluating how a change in the price of a product affects its quantity demanded. A value greater than one indicates **elastic demand**, where consumers significantly reduce their demand with price increases. Conversely, a value less than one suggests **inelastic demand**, indicating minimal changes in quantity demanded regardless of price hikes. Understanding this elasticity measurement aids businesses in predicting **total revenue** impacts and adjusting their marketing strategies accordingly.
Factors Affecting Elasticity
Several factors influence **demand responsiveness** in relation to price changes. Among them are substitutes, necessity versus luxury status, and consumer income levels. For example, products with many substitutes—such as household goods—demonstrate higher elasticity since consumers can easily switch if their preferred brand’s price rises. In contrast, basic necessities like water and bread tend to have inelastic demand as they are essential for daily living regardless of price. Additionally, consumer income plays a pivotal role; higher income typically leads to greater price sensitivity for luxury items but less sensitivity for essential goods. By analyzing these **elasticity determinants**, firms can tailor their pricing strategies.
Calculating Price Elasticity in Practical Scenarios
In real-world applications, businesses often need to estimate elasticity to devise marketing tactics and pricing structures. When making **elasticity calculations**, consider historical data on **demand shifts** and analyze responses to past price changes. This data will guide you on how different quantities respond to price alterations, offering insights into likely future behavior. Furthermore, effective **demand forecasting** strategies allow companies to anticipate market trends and adjust prices to optimize both sales and profit margins.
Step-by-Step Elasticity Calculation
To calculate price elasticity effectively, follow this methodical approach: First, gather the relevant data on **quantity demanded** before and after a price change. For instance, if the price of a product rose from $10 to $12 and quantity demanded fell from 100 to 80 units, the calculations would proceed as follows:
- Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded = ((80 – 100) / 100) * 100 = -20%
- Percentage Change in Price = ((12 – 10) / 10) * 100 = 20%
- Price Elasticity of Demand = -20% / 20% = -1
Here, an elasticity of -1 indicates unitary elasticity, meaning the total revenue remains constant with price changes. This example illustrates how **measuring consumer reactions** can influence pricing strategies and helps in economic analysis.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Many companies utilize **elasticity assessments** to refine their marketing strategies. For example, during a holiday season, retailers might deepen discounts to stimulate demand, directly applying elasticity insights. A classic case is Starbucks, which adjusts its prices strategically based on the anticipated demand elasticity of seasonal drinks versus standard offerings. They closely monitor customer responses to price changes, adjusting production and inventory accordingly. Such real-life elasticity scenarios illustrate how understanding price elasticity can provide strategic advantages in competitive markets.
Implications of Price Elasticity for Businesses
The significance of price elasticity extends well beyond theoretical concepts; practical implications for businesses are vast. Knowing whether a product exhibits **elastic demand** or **inelastic demand** influences pricing decisions, marketing approaches, and inventory management. When setting prices, businesses must also understand the relationship between **price and demand**, ensuring optimal alignment for revenue maximization.
Adjusting Pricing Strategies Based on Elasticity
Understanding the implications of elasticity is fundamental for crafting successful pricing strategies. Companies can adopt various tactics, such as precision pricing or discount strategies, based on elasticity metrics. An example of precise implementation is found in travel industries, where airlines assess demand elasticity closely when adjusting ticket prices based on seasonality and event-driven demand changes. Proactive elasticity planning allows firms to remain responsive to market conditions, ensuring consumer satisfaction while maximizing profit margins.
Correlating Elasticity with Market Trends
Market trends often dictate the pricing dynamics of various commodities. For instance, during economic downturns, products typically regarded as luxury items will observe a decrease in demand, indicating increased elasticity in those segments. On the other hand, necessary goods tend to maintain steady demand. Companies must stay informed of shifting market trends to accurately adjust their **demand analysis** and effectively manage their pricing strategies. In understanding how elasticity trends relate to market forces, businesses can anticipate changes more accurately.
Key Takeaways
- Price elasticity of demand assesses how quantity demanded responds to price changes.
- Numerous factors affect elasticity, including availability of substitutes and the good’s necessity.
- Real-world applications demonstrate the importance of elasticity in strategic pricing decisions.
- Constant adjustments in pricing strategies are vital as market conditions and consumer behaviors change.
- Effective elasticity evaluation provides substantial insight into consumer behavior and helps businesses stay competitive.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of price elasticity of demand?
The significance of price elasticity of demand lies in its ability to inform businesses about consumer responsiveness to pricing changes. Understanding these dynamics helps optimize **demand pricing strategies**, enhancing revenue management and minimizing risk associated with price adjustments. By analyzing price elasticity, firms can more effectively predict how changes in price might impact their sales and overall profitability.
2. How do you measure price elasticity?
Price elasticity can be measured using the formula: Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) = (% Change in Quantity Demanded) / (% Change in Price). This measurement enables businesses to evaluate how sensitive customers are to price changes. An elastic product indicates a significant demand response to price changes, while inelastic items show lesser sensitivity.
3. Can price elasticity be influenced by external factors?
Yes, price elasticity can be significantly influenced by external factors, including consumer income levels, availability of substitutes, and overall market conditions. For example, during economic hardships, consumers may become more price-sensitive, leading to increased elasticity in several markets.
4. How can businesses utilize elasticity in their marketing strategies?
Businesses can employ elasticity insights to design precise marketing strategies by adjusting prices based on elasticity assessments. For example, if demand for a product is highly elastic, a slight reduction in price might attract significantly higher sales volume, subsequently increasing total revenue and enhancing market share.
5. What are some common pitfalls in estimating price elasticity?
Common mistakes when estimating price elasticity include using outdated data, failing to consider substitution effects, or neglecting to account for the broader economic context. Accurate estimates require comprehensive data analysis that captures varying consumer behaviors and market fluctuations related to current pricing strategies.